目次
JPAとは
JPAとはJava Persistence APIの略で、以下の2つの機能をJavaのAPI仕様として定義したものです。
- リレーショナルデータベースで管理されているレコードを、Javaオブジェクトにマッピングする。
- マッピングされたJavaオブジェクトに対して行われた操作を、リレーショナルデータベースのレコードに反映する。
開発環境
開発環境
開発環境は以下の通り。
環境構築手順はこちら ⇒ EclipseでSpring Bootの環境構築 | 分かりやすく図解で説明
| 開発環境 | 名称 | 説明 |
| 開発言語 | Java | 人気の開発言語 |
| 開発ツール | Eclipse | Javaでの定番開発ツール |
| フレームワーク | Spring Boot | 人気のSpringフレームワークをベースとしたフレームワーク |
| テンプレートエンジン | Thymeleaf | Spring Bootと相性が良いテンプレートエンジン |
| データベース | MySQL | フリーで利用できる人気データベース |
ディレクトリ構成
ディレクトリ構成は以下の通り。
springSample
|
|___src.main.java
|
|___com.example.demo
| |
| |___controller
| | |
| | |__UserController.java
| |
| |___entity
| | |
| | |___User.java
| |
| |___repository
| | |
| | |___UserRepository.java
| |
| |___service
| |
| |___UserService.java
|
|___src.main.resources
|
|___templates
| |
| |___user
| |
| |___list.html
|
|___static
|
|___css
|
|___list.css事前準備
データベース接続設定
プロジェクトにある「application.properties」を開き、MySQLの接続情報を設定します。
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost/sampledb
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=password
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driverbuild.gradleの依存関係
プロジェクトにある「build.gradle」を開き、使用する機能と依存関係の設定を行います。
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-jpa'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web'
compileOnly 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
runtimeOnly 'mysql:mysql-connector-java'
annotationProcessor 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
providedRuntime 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-tomcat'
testImplementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test'
}データベースにテーブルとデータの登録
今回は以下のテーブルを作成します。
■ユーザー情報TBL
| 物理名 | 論理名 | データ型 | NOT NULL | 説明 |
| id | ID | BIGINT | 〇 | 主キー(AUTO_INCREMENT) |
| name | 名前 | VARCHAR(100) | 〇 | ユーザーの名前 |
| address | 住所 | VARCHAR(255) | ユーザーの住所 | |
| phone | 電話番号 | VARCHAR(50) | ユーザーの電話番号 | |
| update_date | 更新日時 | DATETIME | 〇 | 最終更新日時 |
| create_date | 作成日時 | DATETIME | 〇 | 登録日時 |
| delete_date | 削除日時 | DATETIME | 論理削除した日時 |
以下のCreate文でテーブルを作成します。
CREATE TABLE `sampledb`.`user` (
`id` BIGINT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
`address` VARCHAR(255) NULL,
`phone` VARCHAR(50) NULL,
`update_date` DATETIME NOT NULL,
`create_date` DATETIME NOT NULL,
`delete_date` DATETIME NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`));以下のInsert文でテーブルにデータを登録します。
INSERT INTO `sampledb`.`user` (`id`, `name`, `address`, `phone`, `update_date`, `create_date`) VALUES ('1', 'テスト太郎', '東京都サンプル区1-1', '080-0000-0000', '2019-05-06 12:00:00', '2019-05-01 12:00:00');バックエンド(サーバ)のソースコード
スポンサーリンク
Entityクラスの作成
データベースから取得したデータを格納するEntityクラスを作成します。
[com.example.demo.entity.User.java]
package com.example.demo.entity;
import java.util.Date;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import lombok.Data;
/**
* ユーザー情報 Entity
*/
@Entity
@Data
@Table(name = "user")
public class User {
/**
* ID
*/
@Id
@Column(name = "id")
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
/**
* 名前
*/
@Column(name = "name")
private String name;
/**
* 住所
*/
@Column(name = "address")
private String address;
/**
* 電話番号
*/
@Column(name = "phone")
private String phone;
/**
* 更新日時
*/
@Column(name = "update_date")
private Date updateDate;
/**
* 登録日時
*/
@Column(name = "create_date")
private Date createDate;
/**
* 削除日時
*/
@Column(name = "delete_date")
private Date deleteDate;
}Repositoryクラスの作成
データベースへアクセスするためのRepositoryクラスを作成します。
[com.example.demo.repository.UserRepository.java]
package com.example.demo.repository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.example.demo.entity.User;
/**
* ユーザー情報 Repository
*/
@Repository
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
}Controllerクラスの作成
フロントエンドとバックエンドの入出力の管理を行うControllerクラスを作成します。
[com.example.demo.controller.UserController.java]
package com.example.demo.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import com.example.demo.entity.User;
import com.example.demo.service.UserService;
/**
* ユーザー情報 Controller
*/
@Controller
public class UserController {
/**
* ユーザー情報 Service
*/
@Autowired
UserService userService;
/**
* ユーザー情報一覧画面を表示
* @param model Model
* @return ユーザー情報一覧画面のHTML
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/user/list", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String displayList(Model model) {
List<User> userlist = userService.searchAll();
model.addAttribute("userlist", userlist);
return "user/list";
}
}Serviceクラスの作成
具体的な処理(ビジネスロジック)を記述するServiceクラスを作成します。
[com.example.demo.service.UserService.java]
package com.example.demo.service;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.example.demo.entity.User;
import com.example.demo.repository.UserRepository;
/**
* ユーザー情報 Service
*/
@Service
public class UserService {
/**
* ユーザー情報 Repository
*/
@Autowired
UserRepository userRepository;
public List<User> searchAll() {
// ユーザーTBLの内容を全検索
return userRepository.findAll();
}
}フロントエンド(画面)のソースコード
HTMLの作成
ユーザーの一覧画面をHTMLで作成します。テンプレートエンジンは「Thymeleaf」を使用しています。
[templates/user/list.html]
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>ユーザー情報一覧</title>
<link href="/css/list.css" rel="stylesheet"></link>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
</head>
<body>
<h1>ユーザー情報一覧</h1>
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>ID</th>
<th>名前</th>
<th>住所</th>
<th>電話番号</th>
<th>更新日時</th>
<th>登録日時</th>
<th>削除日時</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr th:each="user : ${userlist}" th:object="${user}">
<td class="center" th:text="*{id}"></td>
<td th:text="*{name}"></td>
<td th:text="*{address}"></td>
<td class="center" th:text="*{phone}"></td>
<td class="center" th:text="${#dates.format(user.updateDate, 'yyyy/MM/dd')}"></td>
<td class="center" th:text="${#dates.format(user.createDate, 'yyyy/MM/dd')}"></td>
<td class="center" th:text="${#dates.format(user.deleteDate, 'yyyy/MM/dd')}"></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</body>
</html>CSSの作成
HTMLで読み込むスタイルシート(CSS)を作成します。
[static/css/list.css]
table {
width: 90%;
border-collapse: collapse;
font-size: 12px;
}
table th, table td {
border: 1px solid #ddd;
padding: 6px;
}
table th {
background-color: #F2F2F2;
}
.center {
text-align: center;
}スポンサーリンク
Webアプリケーションの実行
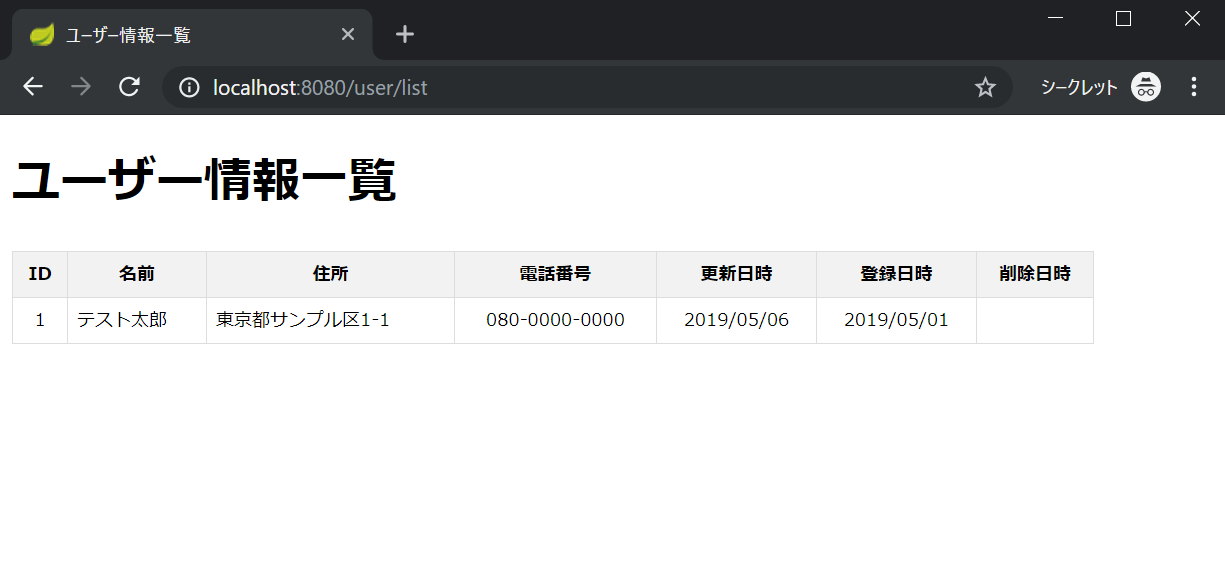
Spring Bootプロジェクトを実行して http://localhost:8080/user/list へアクセスします。
以下の画面が表示されれば、完了です。
終わりに
本記事では「Spring Boot+JPAでデータベースに接続する方法」を行う手順について紹介しました。
次回は、JPAではなくMyBatisを利用したアプリケーションの作り方を紹介します。
- 準備編 EclipseでSpring Bootの環境構築 | 分かりやすく図解で説明
- 第一章 Spring Boot+Thymeleafで”Hello World”を作成する
- 第二章 Spring Boot+JPAでデータベースに接続する方法
- 第三章 Spring Boot+MyBatisでデータベースに接続する

